Search
News & Events
Join our Weight & Body Composition Working GroupInterested in research into weight and body composition?

News & Events
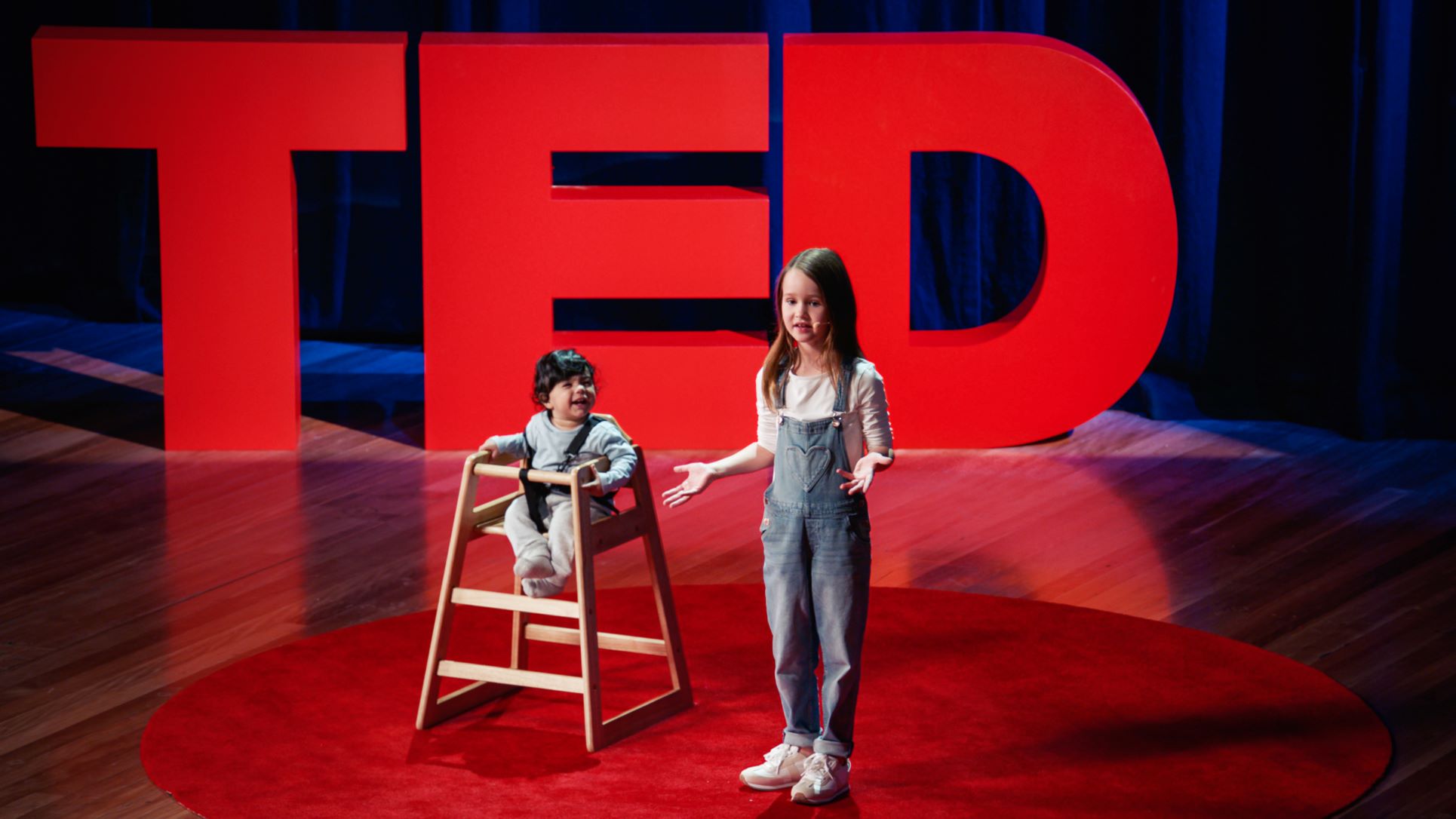
Thrive by Five TED Talk - Have you met Molly?ORIGINS Director, Prof Desiree Silva is playing an integral role in promoting a Thrive by Five TED Talk asking parents to engage more meaningfully and often with children in order to promote their brain development and set them up for life.

News & Events
COVID-19 Update: 27 June 2021COVID-19 27 June 2021 Update: It is business as usual for ORIGINS, though masks must be worn.

News & Events
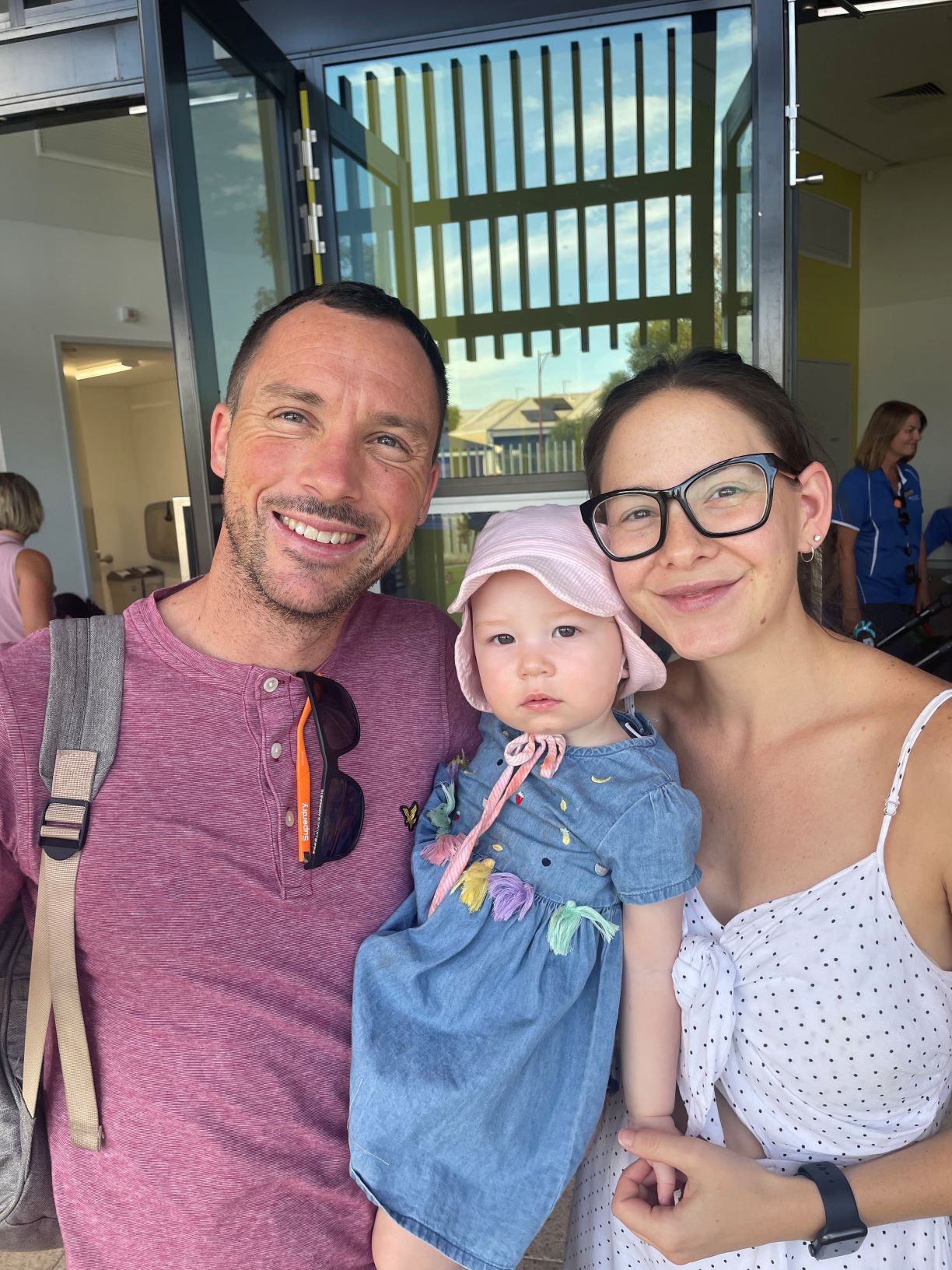
ORIGINS Family Day 2021ORIGINS says thank you to our gorgeous families with a Family Fun Day at the Pearsall Hocking Community Centre.

News & Events
ORIGINS Adventures at the Telethon Family FestivalWe loved seeing so many families at the ORIGINS marquee at the Telethon Family Festival at Optus Stadium

News & Events
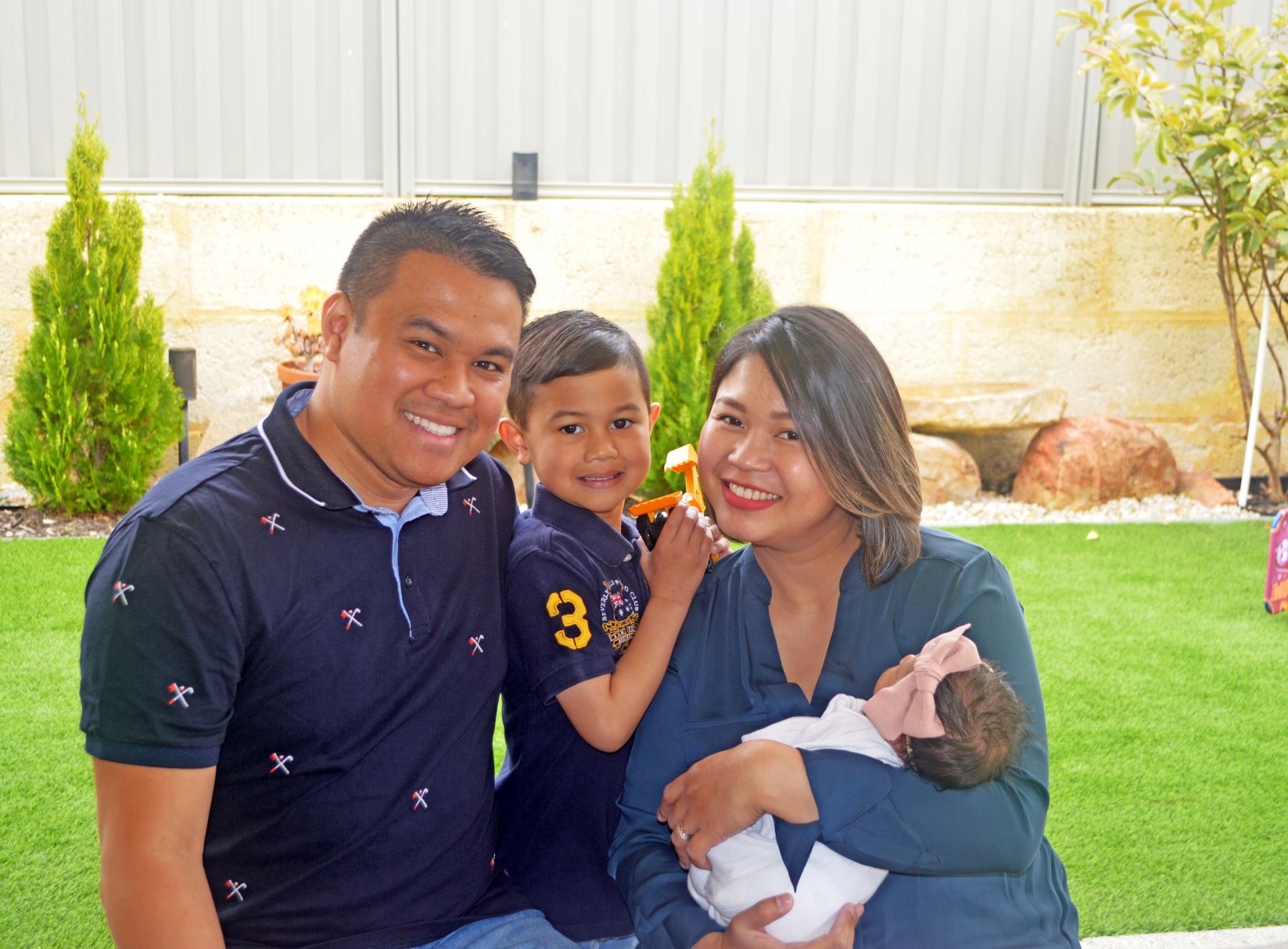
ORIGINS has welcomed its 4,000th familyORIGINS has recently welcomed its 4,000th family into the study.
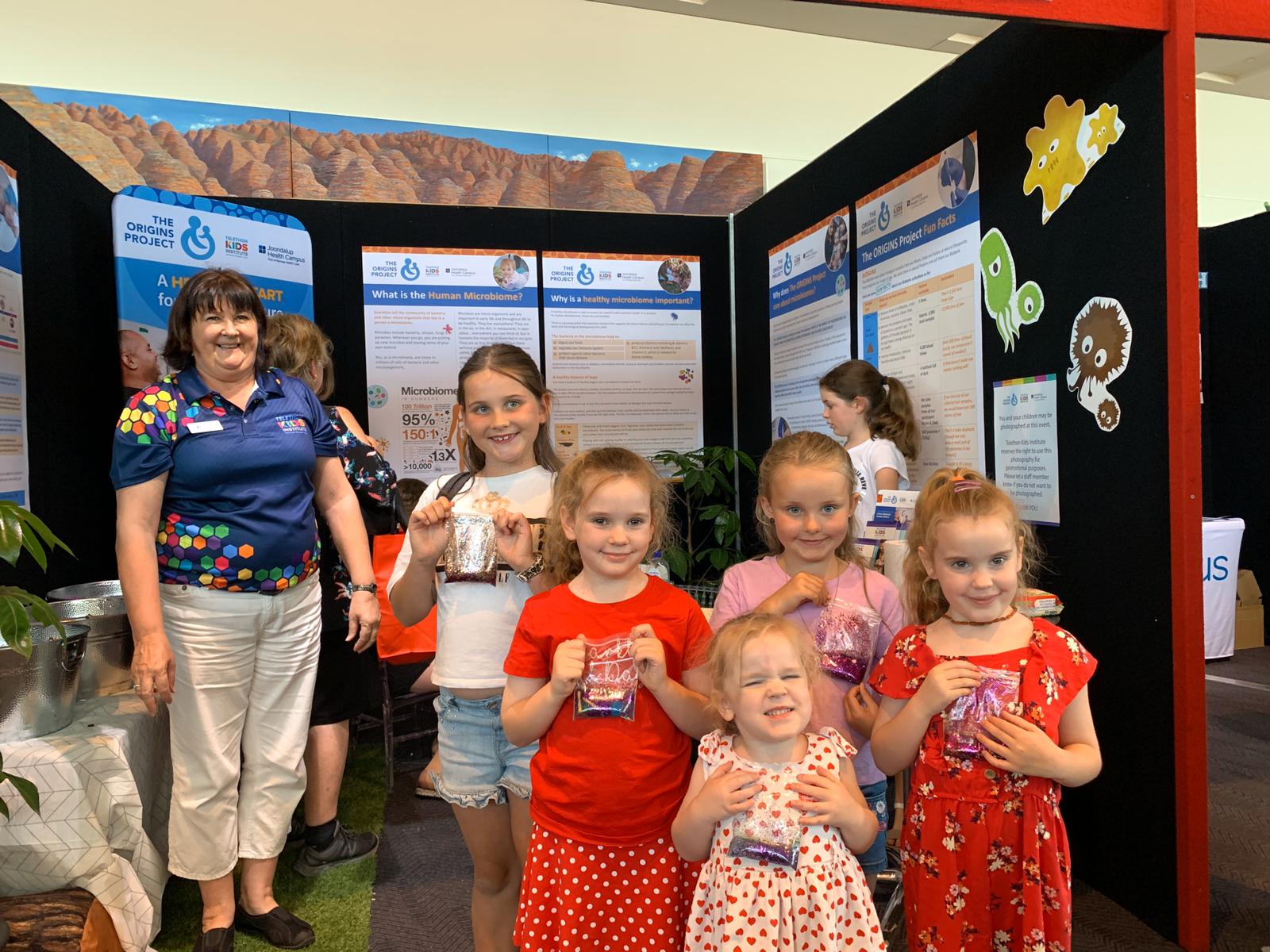

News & Events
Magical Microbiomes at TelethonHundreds of kids and their families visited The ORIGINS Project booth over the Telethon weekend to learn about the magical microbiome.
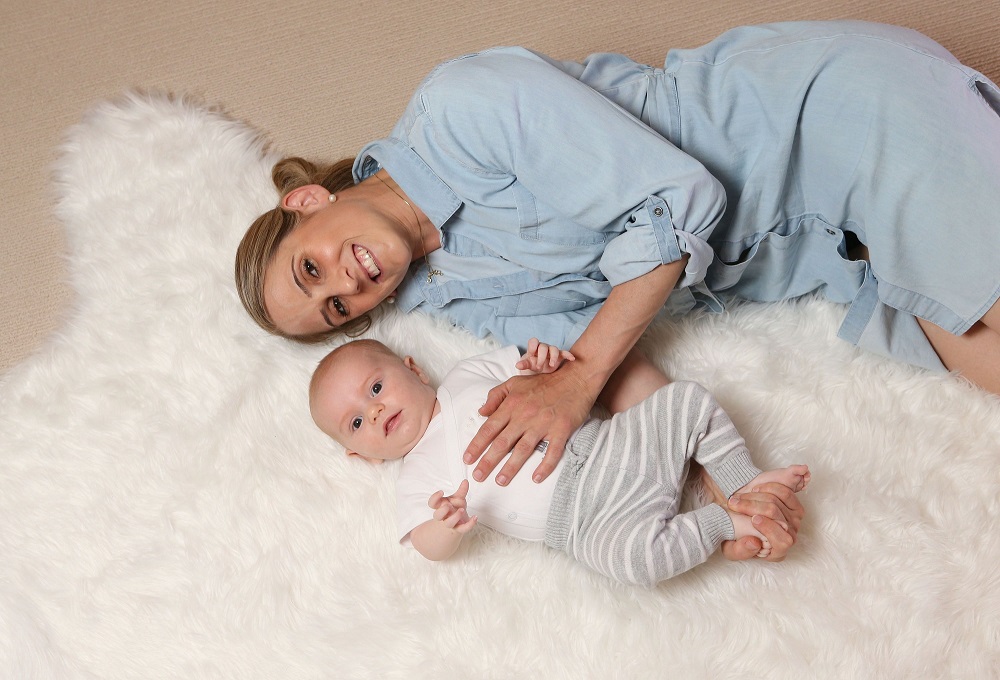

News & Events
World-first research helps to identify child developmental delaysThe ORIGINS Project’s Early Moves study is investigating whether a baby’s early movements can predict learning difficulties later in childhood.
News & Events
Q&A with Dr Michael MosleyDr Michael Mosley recently visited The Kids Research Institute Australia to talk about DOHaD and the importance of good gut health.

News & Events
Tech use impact on child health probed in ORIGINS studyA possible link between a rise in conditions such as obesity and attention deficit disorder and the use of computers and smartphones is the focus of a new ORIGINS Project sub-study into the effects of technology on children’s development.
